What is people flow simulation?
Crowd simulation makes it possible to model the behaviour of crowds in different environments such as airports, train stations, shopping centres or event venues. It can be used to realistically depict both normal movement patterns and evacuation scenarios.
People flow simulation ensures satisfied customers and faster processes
Escape and evacuation scenarios are classic areas of application for people flow simulation. In particular, facilities with a high density of people, such as sports halls or stadiums, are investigated with regard to various damage events and the resulting necessities for the provision of routes and escape doors, taking into account real human behavior. People move according to the same scientifically verified rules, but depending on their directly perceivable environment.
This results in individual movement patterns which, in a group, lead to phenomena that are no longer macroscopically calculable. This is where simulation comes into play, in order to ensure escape in the event of damage within the time frame usually prescribed by law. This is all the more important because such scenarios cannot be played out with reasonable effort and realistic conditions, e.g. with extras. Simulation is often the only option here.
Advantages and benefits of crowd simulation
- Testing security concepts: Simulate evacuation scenarios to understand how people behave in emergency situations and to identify bottlenecks or risks at an early stage.
- Increasing efficiency: Optimise the utilisation of rooms and routes to minimise waiting times and ensure the smooth movement of people.
- Increasing customer and employee satisfaction: Optimised people flows help to avoid bottlenecks and improve the experience for everyone involved.
- Planning security: Make informed decisions when designing and adapting infrastructures based on precise simulation data.
Typical areas of application
- Event venues (stadiums, concert halls, trade fairs)
Pedestrian flow simulation helps to analyse the movements of large crowds at events. This way, bottlenecks at entrances and exits, waiting areas and escape routes can be optimised to improve safety and the visitors’ experience. - Train stations and airports
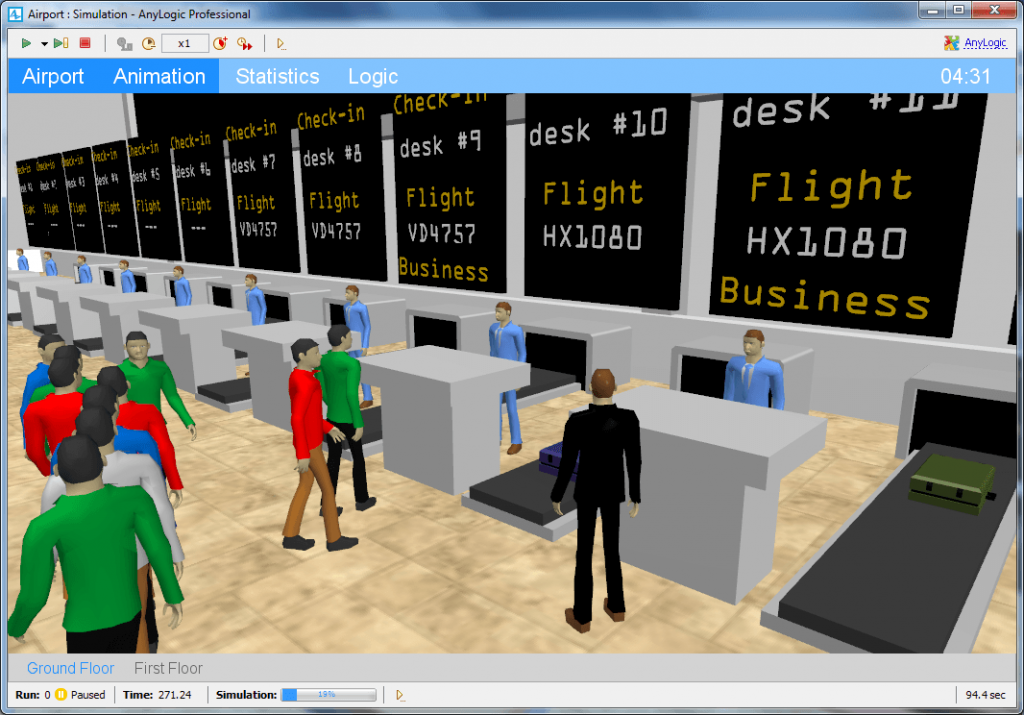
At transport hubs, simulation ensures that passenger flows are efficiently routed through security checkpoints, queues, gates and platforms. It also helps to reduce waiting times and prevent bottlenecks at peak times. - Shopping centres and retail
By simulating customer flows, shopping centre operators can optimise the layout of their shops, corridors and entrance areas. The aim is to improve the flow of customers, reduce waiting times at checkouts and create a pleasant shopping experience. - Museums and theme parks
In areas with many visitors, simulation helps to direct visitor flows, avoid bottlenecks in popular areas and increase comfort and safety. This can also lead to better visitor guidance and increased capacity utilisation. - Evacuation scenarios in buildings
In high-rise buildings, offices or production plants, simulation can be used to optimise evacuation plans. It enables the testing of emergency scenarios and helps to design efficient escape routes and minimise risks. - Urban planning and public spaces
In urban infrastructure planning, pedestrian flows are simulated to optimise the design of sidewalks, intersections, parks and public transportation. This helps to guide crowds safely and efficiently through urban spaces. - Hospitals and healthcare centres
In hospitals, pedestrian flow simulations can help optimise patient flows in waiting areas, treatment rooms and emergency rooms. This helps to improve organisational efficiency and patient safety. - Research and development of building layouts
Architects and planners use simulations to understand how people will behave in planned buildings or infrastructure and to design the layout for efficient use. For example, stairwells, lifts and emergency exits can be optimally placed. - Mass gatherings in the open air (e.g. festivals, sporting events)
For outdoor events, simulation can be used to predict potential bottlenecks at entrances, food stands or toilets. It can also help to develop evacuation strategies in the event of severe weather or other emergencies. - Industrial sites and production facilities
In factories or production plants, simulation can be used to analyse the flow of people of workers. This allows better planning and organisation of work routes, break areas and safety equipment.
Each of these use cases shows how flexibly people flow simulation can be used to achieve both safety and efficiency gains.
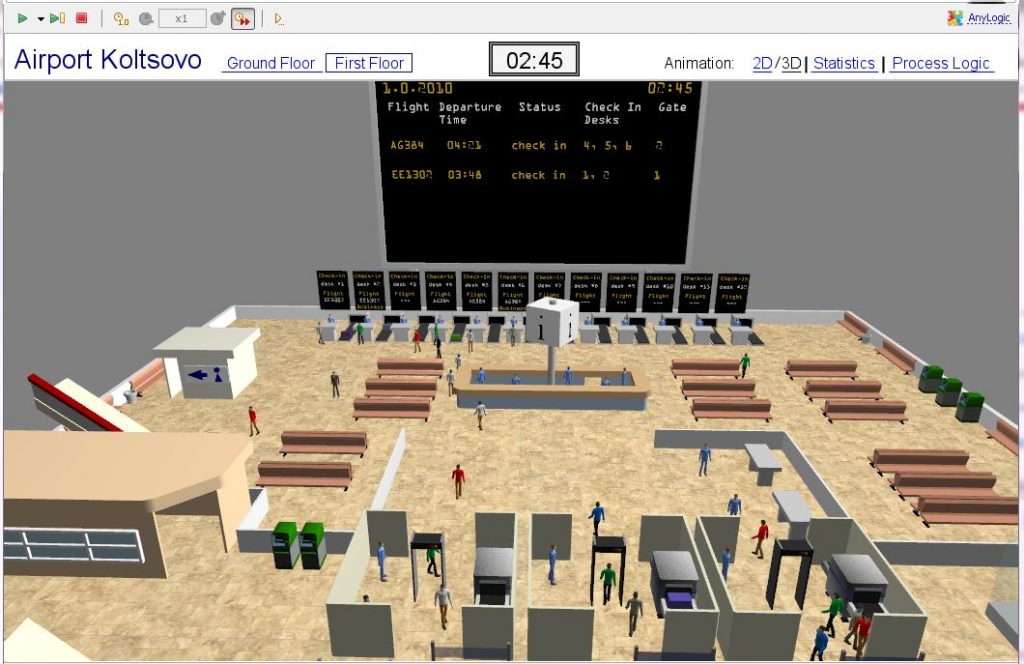
Example model passenger flow simulation
Entrance area of a subway station
Sie sehen gerade einen Platzhalterinhalt von Standard. Um auf den eigentlichen Inhalt zuzugreifen, klicken Sie auf den Button unten. Bitte beachten Sie, dass dabei Daten an Drittanbieter weitergegeben werden.
